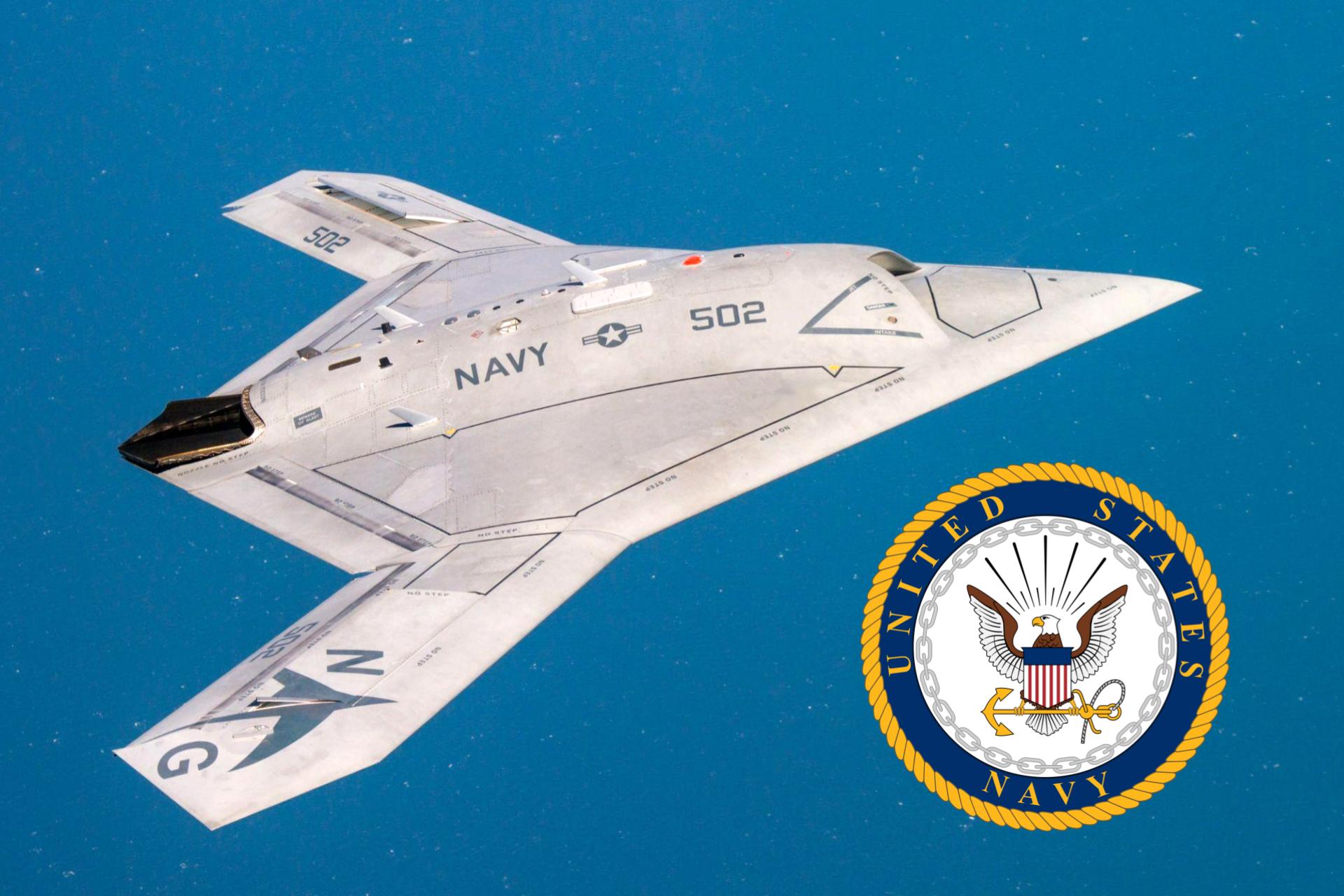
HLS.Today – The Northrop Grumman X-47B is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) designed and developed by Northrop Grumman for the United States Navy. The X-47B is a part of the Navy’s Unmanned Combat Air System Demonstration (UCAS-D) program, which aimed to demonstrate the feasibility of using UAVs in carrier-based operations. In this article, we will discuss the development, financing, testing, and flight history of the X-47B, along with details about its components.
Development and Financing:
The development of the X-47B began in 2005, when the U.S. Navy awarded a contract to Northrop Grumman for the UCAS-D program. The program was aimed at developing a UAV that could operate from an aircraft carrier and perform a variety of missions, including surveillance, reconnaissance, and strike operations.
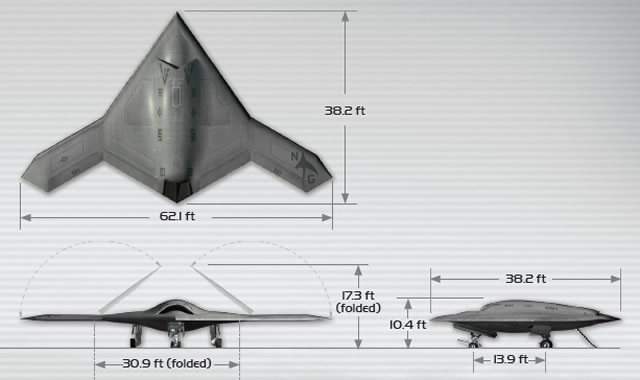
The X-47B was designed to be a stealthy, tailless aircraft with a wingspan of 62 feet and a weight of approximately 14,000 pounds. The drone is powered by a Pratt & Whitney F100-PW-220U engine and can reach a maximum speed of 0.9 Mach. The X-47B is also equipped with a variety of sensors, including a multi-function active sensor radar, electro-optical and infrared sensors, and a communication system.
The development of the X-47B was financed by the U.S. Navy, which allocated approximately $1.4 billion for the UCAS-D program. Northrop Grumman also contributed to the funding of the project, investing approximately $1 billion of its own money.
Testing:
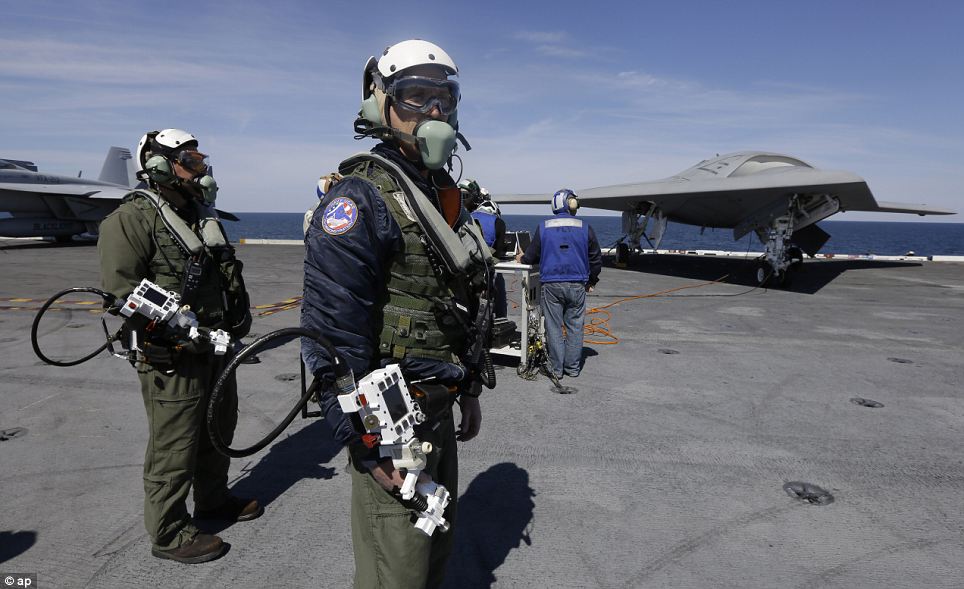
The X-47B underwent a series of tests and demonstrations before it was deemed ready for operational use. The testing phase began in 2011 and included a variety of ground tests and flight tests.
The first flight of the X-47B took place in 2011 at Edwards Air Force Base in California. The drone was launched and recovered from a land-based catapult and arrested landing system. In 2013, the X-47B made history by becoming the first UAV to take off and land from an aircraft carrier, the USS George H.W. Bush.
During the testing phase, the X-47B demonstrated its ability to perform a variety of missions, including autonomous takeoff and landing, aerial refueling, and strike operations. The drone also demonstrated its ability to operate in a variety of weather conditions and navigate through a complex flight path.
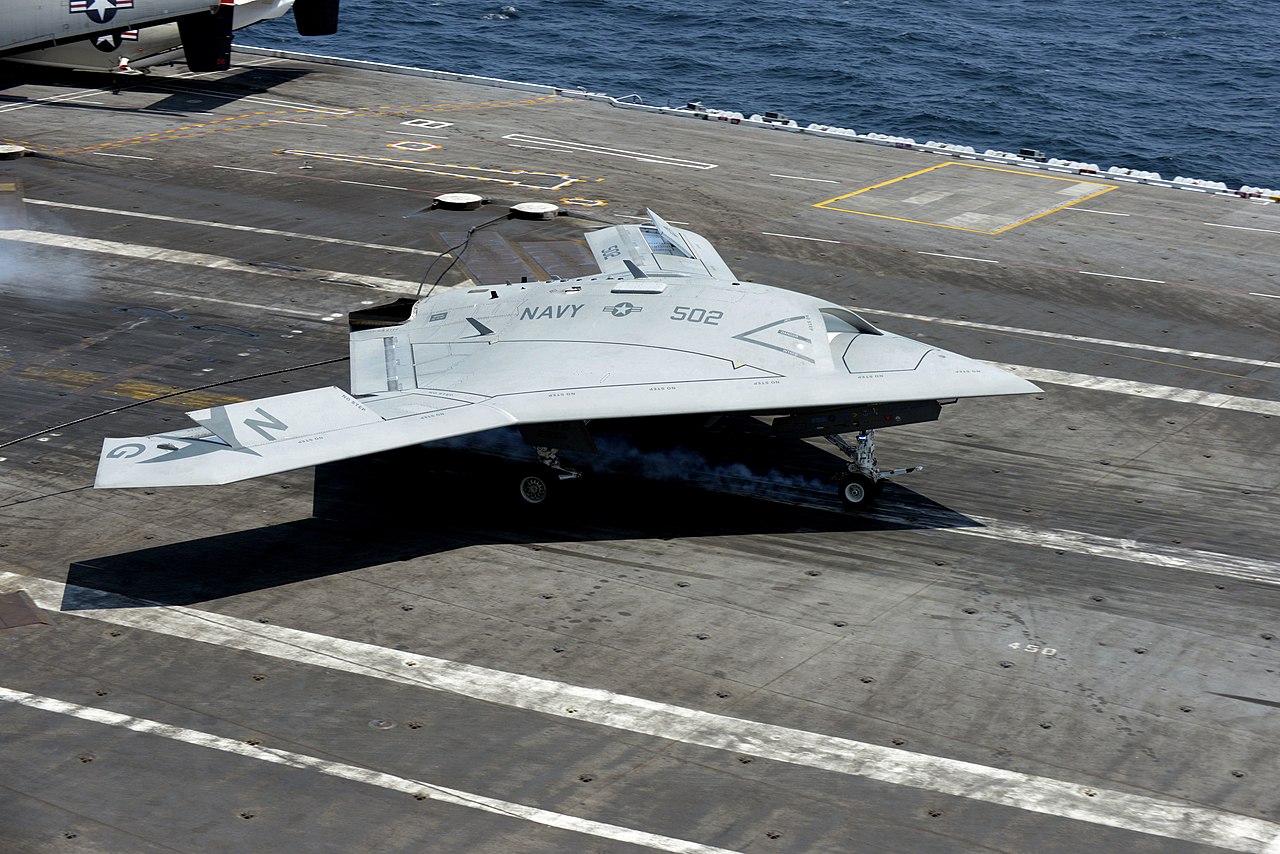

Flight History:
The X-47B was used in a variety of operational tests and demonstrations before it was retired in 2015. During its operational history, the drone was used to perform a variety of missions, including surveillance, reconnaissance, and strike operations.
One of the most notable missions performed by the X-47B was the Autonomous Aerial Refueling (AAR) demonstration, which took place in 2015. During this mission, the X-47B successfully received fuel from a manned tanker aircraft, demonstrating its ability to operate in a complex, dynamic environment.
The X-47B was retired from service in 2015, and its technology was used to develop the Navy’s MQ-25 Stingray, which is currently in development.
Components:
The X-47B is a complex aircraft with a variety of components that work together to enable its mission capabilities. Some of the key components of the X-47B include:
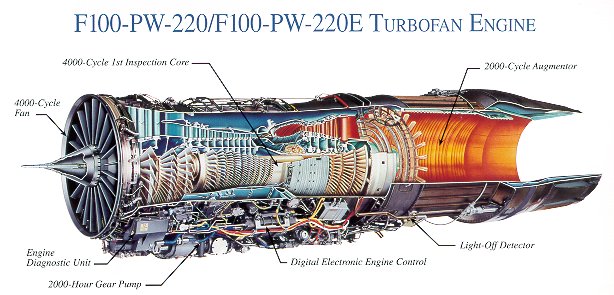
- Pratt & Whitney F100-PW-220U engine: The X-47B is powered by a Pratt & Whitney F100-PW-220U engine, which provides the drone with a maximum speed of 0.9 Mach.
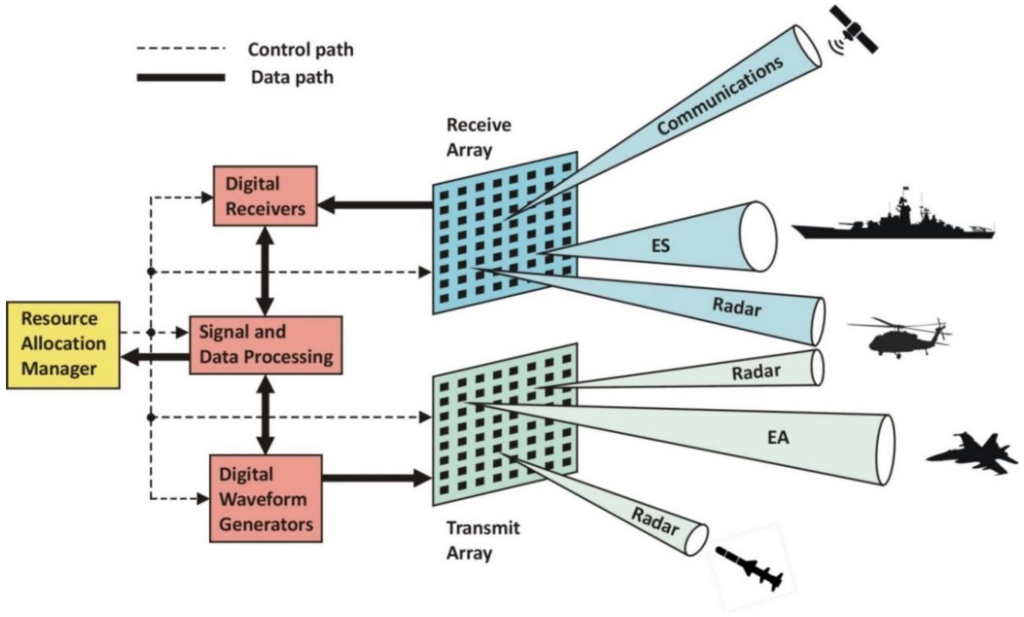
- Multi-function active sensor radar: The X-47B is equipped with a multi-function active sensor radar, which allows the drone to detect and track targets on the ground and in the air.
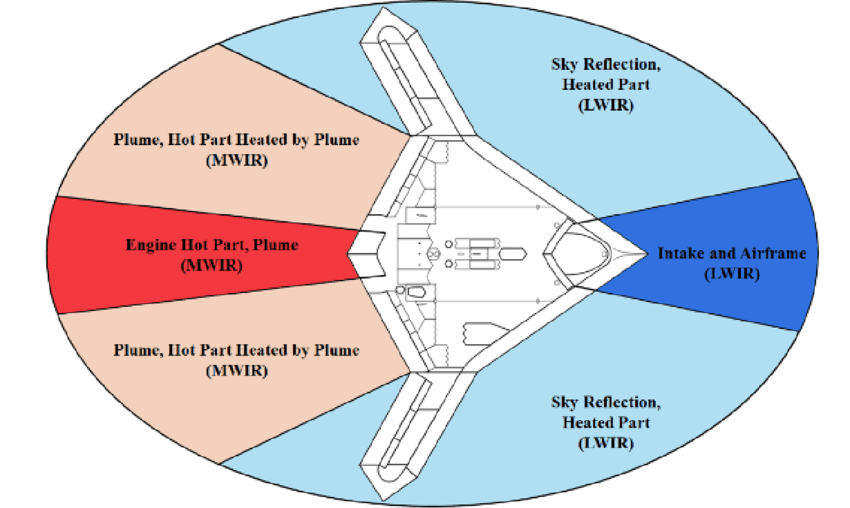
- Electro-optical and infrared sensors: The X-47B is also equipped with electro-optical and infrared sensors, which provide the drone with the ability to conduct surveillance and reconnaissance missions.
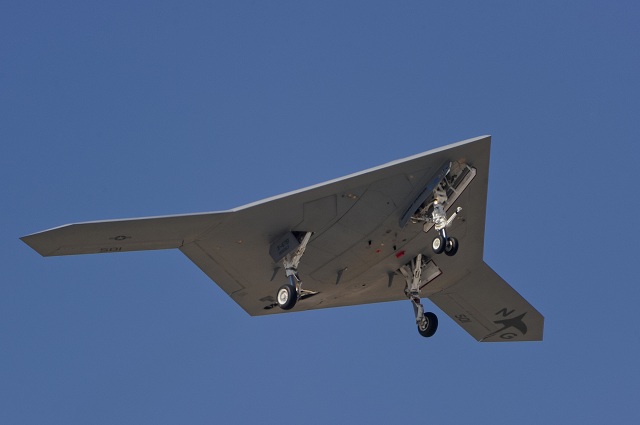

- Communication system: The X-47B is equipped with a communication system that allows it to communicate with other aircraft and ground-based control systems.

- Stealth technology: The X-47B was designed with stealth technology, including a low radar cross-section and a reduced infrared signature, to make it less detectable by enemy forces.
Conclusion:
The Northrop Grumman X-47B is a groundbreaking UAV that played a crucial role in the development of carrier-based UAV operations for the U.S. Navy. The drone’s development, financing, testing, and flight history demonstrate the Navy’s commitment to exploring new technologies and capabilities to meet evolving threats. With its advanced components and capabilities, the X-47B paved the way for the development of future UAVs and will continue to have a lasting impact on the Navy’s unmanned aircraft programs.
HLS.Today Source: US.Navy







